Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a pivotal role in India's economic landscape, especially in the manufacturing sector. These enterprises create various economic opportunities in both rural and urban areas. Recognizing this, the government has launched several initiatives aimed at making India “Atma Nirbhar” (self-reliant) and achieving the goal of contributing 25% to the nation’s GDP.
It highlights the significance of SMEs in the manufacturing industry and outlines actionable strategies for achieving growth.
The small and medium enterprises (SMEs) sector in India has emerged as a powerhouse, fueling the nation’s economic growth by driving employment generation in the domestic market, boosting export, fostering innovation and inclusive development. Often hailed as the backbone of India’s socio-economic growth, the sector focuses on driving industrialization in underdeveloped areas, facilitating fair distribution of income and wealth across the country.
In India, SMEs play a important role in both the manufacturing and service sectors. The manufacturing industry is an emerging pillar of India’s socio-economic environment. With a contribution of 17% to the nation’s GDP and employing over 27.3 million workers, the sector has driven commendable economic growth, especially in rural India, by creating job opportunities, expanding exports and promoting innovation, leading to increased productivity and economic growth.
As the Indian manufacturing sector is projected to be one of the fastest growing sectors, the government hopes to have 25% of the economy’s output come from manufacturing by 2025, aligning with the “Make in India” vision. Let's delve deeper to discover how SMEs in the manufacturing sector can turn their vision into reality.
Did you know? : “India has the largest SME base in the world after China, with 63.05 million micro industries, 0.33 million small, and about 5,000 medium enterprises in the country.”
The SME landscape in India
India's SME sector is experiencing diversity, with a growing number of manufacturing and service sectors. With the number of SMEs registered on the Udyam portal recently reaching an impressive 4,00,42,875, SMEs in India are emerging at an unprecedented pace. This remarkable growth is not only fostering entrepreneurship but also generating self-employment opportunities to millions of individuals across the nation.
It is estimated that the market size of SMEs is expected to expand more in subsequent days to 7.5 crore. To support the growth, the Ministry of Finance has allocated Rs. 22,137.95 crores (US$ 2.65 billion) for SMEs, emphasizing on cluster development and technology centers for global competitiveness.
These small-scale enterprises are widening their domain across sectors of the economy, producing a diverse range of manufacturing output to meet demands of domestic as well as global markets, mainly in sectors like Textile, Automotive, Pharmaceuticals and Electronics, which also contributes majorly to the GDP of the nation.
The following data shows how automotive and textile industries have been contributing 6% and 2.3% to the nation’s GDP, respectively. While pharmaceuticals contribute 2% and electronics 3.4% to the nation's GDP.
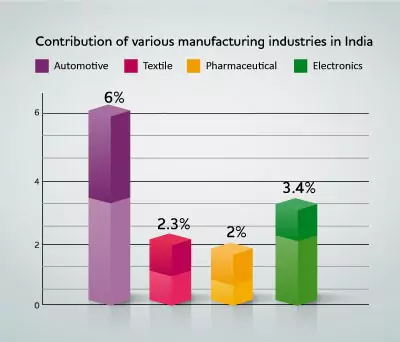
These sectors in the manufacturing industry can significantly boost industrial growth and economic development by promoting strategies on skill development, infrastructure development, technology upgradation, global market access, export promotion and investment attraction, for which the government has extended its support to empower SMEs through the following initiatives discussed subsequently below:
Leveraging government initiatives for SME growth
To help SMEs grow in the manufacturing sector, the Indian Government has launched several initiatives, with an aim to strengthen the market economy and drive sustainable development. Here are some of the key government initiatives pushing for SMEs growth.
Prime Minister's employment generation program (PMEGP) : The PMEG scheme provides financial assistance for setting up new enterprises in both rural and urban areas. It also aims to create jobs by setting up micro enterprises, targeting mainly the traditional artisans and unemployed youth.
-
Scheme of fund for regeneration of traditional industries (SFRUTI) : The SFRUTI initiative aims to organise traditional industries into competitive clusters, provide sustained employment, enhance product marketability, improve skills through training, and promote innovative technologies and partnerships.
-
Strengthening of pharmaceutical industry (SPI) : The SPI scheme addresses the demands of support required to existing Pharma clusters and SMEs, to improve their productivity, quality and sustainability by fostering resilience and future-readiness in the existing infrastructure facilities.
-
A Scheme for promotion of innovation, rural industries, and entrepreneurship (ASPIRE) : : ASPIRE aims to promote rural innovation and entrepreneurship, support agriculture and rural startups, enhance skill development, facilitate finance and market access.
-
Micro and small enterprises – Cluster development programme (MSE-CDP) : The scheme helps SMEs to enhance the productivity and competitiveness by adopting cluster approach through financial assistance from the government for the establishment of Common Facility Centers (CFCs) in the existing clusters and for new establishment or upgradation of existing industrial areas.
-
Procurement and marketing support scheme (PMS) : The Procurement and Marketing Support Scheme aims to develop domestic markets for SMEs, facilitate market linkages under the Public Procurement Policy, educate SMEs on business development, and raise awareness about trade fairs and market techniques.
-
Raising and accelerating MSME performance (RAMP) : : This scheme aims to make SMEs competitive and self-reliant in the states by fostering innovation, encouraging ideation, incubating new entrepreneurship by developing quality standards, deploying technological tools and enhancing market access.
-
Capacity building of first-time MSME exporters (CBFTE) : :The capacity building scheme supports new SME exporters by providing training, compliance guidance, marketing assistance, and access to resources for enhancing export capabilities.
PLI schemes and impact on SMEs
Additionally, to boost domestic manufacturing and promote the SME ecosystem, the government introduced the central scheme of Production Linked Incentive (PLI) with an aim to enhance production volumes and improve competitiveness.
This also includes supply of goods/services while starting or closing a business.
The PLI scheme has helped scaling up production and improving product quality. The initiative led to sales worth Rs 8.7 lakh crore and generated employment for over 7 lakh individuals, which has benefitted 176 SMEs to boost its production in the country.
The advent of the scheme has broadened the scope of manufacturing sector and created a significant impact through the following ways:
- Supporting the MSME ecosystem
- Encouraging design-based manufacturing
- Boosting OEM manufacturing
- Actionable strategies for SMEs
The PLI scheme can boost the overall manufacturing ecosystem and have a big impact on the SMEs. The scheme provides funding for affordable technologies, innovations, employment generation by foreign companies that can help them compete globally, thereby strengthening partnerships with larger players and enhancing their production capacity.
The PLI scheme encourages design-based manufacturing by providing financial incentives for both domestic and global companies. The scheme includes higher incentive rates for design-led manufacturing compared to traditional manufacturing, encouraging companies to integrate more design and innovation into their processes.
The scheme also encourages Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) to scale up their manufacturing capacities by offering financial incentives, based on the goods’ incremental sales. Like design-based manufacturing, PLI also provides higher incentives for products with greater value addition, to focus on high-quality manufacturing, thereby increasing its export potential.
For SMEs in India to thrive in a competitive market, adopting actionable strategies is crucial. By integrating these strategies, manufacturing enterprises can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and drive sustainable growth through the following means :
Technological advancements and SMEs
In a rapidly changing business environment, almost every sector in India has adopted digital transformation for its inclusive development. As the manufacturing sector of SMEs continues to grapple with numerous challenges, from infrastructure deficiencies to limited technological advancements, it’s time now for SMEs also to embrace emerging technologies to respond to market shifts and meet customer demands.
Embracing current market trends, technology and digital transformation can benefit the sector significantly to :
- Increase its Production Capacity
- Streamline the Workflow Process
- Facilitate Better Customer Experience
- Make Data-Driven Decisions
- Promoting Innovation
To bring a comprehensive solution to the prevailing challenges faced by SMEs, TCS BizHub has joined hands in their journey towards digital transformation and growth. TCS iON's BizHub is a cutting-edge digital platform that aims to empower businesses by offering a comprehensive and cost-effective suite of solutions. It helps organisations streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and drive digital transformation.
For example, Company A buys Raw Material X to manufacture Product Y and pays ₹100 as GST while purchasing X. This ‘input tax’ can be taken as credit and adjusted against GST payable on the value of Product Y sold. GST has four main tax rates: 5%, 12%, 18% and 28% as defined by the Government through the GST Council.
How TCS BizHub facilitates digital transformation for SMEs?
Adoption of new technologies can help the manufacturing sectors of SMEs stay relevant, boost revenue and increase efficiency, while also reducing costs and improving productivity. In this regard, TCS Bizhub works as a catalyst for SMEs’ digital transformation by offering a package of affordable and accessible solutions.
TCS Bizhub can provide a holistic solution to traditional business operations of SMEs by eliminating manual processes, poor customer experience and operational losses with their technology-driven products and services that involves:
1. GST Compliance Solutions: BizHub’s GST compliance solutions help SMEs stay updated with the complex GST regulations and avoid costly penalties. By automating the entire compliance process, the software eases the burden of compliance by saving time and resources, minimizing errors, and enhancing accuracy.
2. Multi-functional ERP : BizHub’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions provide a complete overview of business operations, empowering SMEs to make more informed decisions. This tool securely handles documents, offers valuable insights into financial inventories, customer data and improves financial outcomes while fostering stronger customer relationships. Bizhub’s ERP also deals in human resource management and employee self-service for better workforce management.
ROI and efficiency gains for technology adoption
Emerging technologies provide limitless opportunities for businesses of all sizes and industries. Technology adoption can be a game-changer for SMEs, offering significant returns on investment (ROI) and efficiency improvements. Let's delve into the key areas that Bizhub products provide :
| Technology | ROI benefits | Efficiency gains |
|---|---|---|
| ERP software for manufacturing |
|
|
| GST compliance solution. |
|
|
What SME businesses need to know?
-
Keeping Up with changing trends : As market trends evolve rapidly and businesses that adapt to these changes are more likely to succeed. SMEs in India need to stay vigilant to these shifts, remain informed of customer needs, foster technological innovation and enhance their competitiveness by taking advantage of the government initiatives required for their business needs.
-
Developing qualities : : Maintaining top-notch product quality is crucial for the manufacturing sector to meet customer satisfaction and build trust. SMEs in India should focus on developing high-quality products to gain global access, increase their export and enhance their competitiveness.
-
Prioritising customer satisfaction : SMEs should prioritise building strong customer relationships, as customer satisfaction boosts retention. Customer retention is difficult but important enough to keep businesses running. Excellent customer service plays a key role in sustenance and ensuring business longevity.
Conclusion :
Achieving the target of 25% GDP contribution by 2025 for SMEs in manufacturing requires a multifaceted approach. For this, stakeholders must stay informed about the government policies and implement them effectively. To keep pace with the current market trend, the industry should also focus on forming clusters, enhancing skills and ensuring access to capital.
Furthermore, it is also crucial for the manufacturing sectors of SMEs to break free from conventional methods and seize the opportunities through government schemes and technological solutions to become self-reliant and ultimately achieve economic prosperity.
In this regard, TCS BizHub can significantly boost business productivity and efficiency with their software tools and cutting-edge technology products. To learn more and be a part of our growing community, Register on TCS iON BizHub today.
